House Plans For Houses On Stilts: Design Considerations and Architectural Insights
Houses on stilts, also known as pile dwellings or elevated houses, represent a unique architectural solution primarily employed in regions prone to flooding, unstable soil conditions, or specific geographical constraints. These structures, built on elevated supports or piles, offer numerous advantages, including protection from water damage, improved ventilation, and a lessened environmental impact. The design and construction of houses on stilts require careful planning and consideration of various site-specific factors. This article explores the critical aspects of house plans for houses on stilts, providing an understanding of the structural, environmental, and aesthetic considerations involved.
Site Assessment and Foundation Design
The initial and perhaps most crucial step in developing house plans for houses on stilts is conducting a thorough site assessment. This assessment involves analyzing various factors, including the soil type, water table level, flood risk, and local climate conditions. Soil analysis is essential to determine the load-bearing capacity of the ground and to select appropriate pile materials and installation methods. For instance, in areas with soft or unstable soil, deeper and more robust piling systems may be required. Conversely, areas with rocky or dense soil may allow for shallower and less extensive foundations.
Flood risk assessment is another critical aspect of site evaluation. Historical flood data, hydrological surveys, and elevation maps are utilized to determine the maximum anticipated flood level. This information dictates the minimum height of the stilts, ensuring that the habitable areas of the house remain above the projected floodwaters. Furthermore, the design must account for wave action and debris impact, which can exert significant horizontal forces on the structure. In coastal areas, houses on stilts may need additional reinforcement to withstand storm surges and high winds.
The design of the foundation, including the type, spacing, and depth of the piles, is paramount to the structural integrity of the house. Common pile materials include timber, concrete, steel, and composite materials. Timber piles, often treated to resist decay and insect infestation, are suitable for lighter structures and less challenging soil conditions. Concrete piles offer superior strength and durability, making them appropriate for larger and heavier houses. Steel piles provide high load-bearing capacity and are often used in areas with deep water or unstable subsoil. Composite piles, manufactured from a combination of materials like fiberglass and resin, offer a balance of strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
The spacing of the piles is influenced by the load distribution of the house and the load-bearing capacity of the soil. Closer pile spacing provides greater support and reduces deflection, while wider spacing minimizes the number of piles and can reduce construction costs. A structural engineer typically performs detailed calculations to determine the optimal pile layout, ensuring that the house can withstand anticipated vertical and horizontal loads.
Structural Considerations and Material Selection
The structural design of a house on stilts must address the unique challenges posed by its elevated construction. Unlike conventional houses built on solid foundations, houses on stilts are subject to increased vulnerability to wind loads, seismic activity, and differential settlement. The structural system must be designed to resist these forces and to maintain the stability and integrity of the building.
Wind loads are a significant consideration, particularly in coastal areas and regions prone to hurricanes or strong winds. The design must account for both the direct pressure of the wind on the building's surfaces and the uplift forces that can occur on the underside of the elevated structure. This often necessitates the use of reinforced connections between the piles and the house frame, as well as bracing systems to enhance lateral stability. Additional structural elements, such as shear walls and moment frames, may be incorporated to distribute wind loads and prevent excessive swaying or deformation.
Seismic activity presents another challenge for houses on stilts, especially in earthquake-prone regions. The design must provide adequate resistance to ground motion, preventing collapse and minimizing damage. This may involve the use of flexible connections between the piles and the house frame, allowing the structure to move independently during an earthquake. Seismic isolation systems, which isolate the building from the ground motion, can also be employed to reduce the impact of earthquakes on the structure. Damping devices, which dissipate energy during seismic events, can further enhance the building's resilience.
Differential settlement, which occurs when different parts of the foundation settle at different rates, can also pose a threat to the structural integrity of houses on stilts. This can be caused by variations in soil conditions, uneven loading, or changes in groundwater levels. To mitigate the risk of differential settlement, the foundation design should ensure uniform load distribution and provide adequate support for all parts of the house. This may involve the use of interconnected pile systems or the installation of ground improvement techniques, such as soil compaction or chemical stabilization.
Material selection plays a critical role in the durability and longevity of houses on stilts. Materials should be chosen for their resistance to moisture, insects, corrosion, and other environmental factors. Treated timber, galvanized steel, and durable concrete are commonly used for the structural components of the house. For the cladding and roofing, materials such as fiber cement siding, metal roofing, and composite decking offer excellent weather resistance and require minimal maintenance.
Architectural Design and Functionality
Beyond the structural and engineering considerations, the architectural design of a house on stilts presents unique opportunities for creating functional and aesthetically pleasing living spaces. The elevated platform provides panoramic views, natural light, and cross-ventilation, enhancing the comfort and enjoyment of the home. The space beneath the house can be utilized for parking, storage, or recreational purposes, maximizing the efficiency of the site.
The design of stairs and ramps is an important aspect of the architectural plan, ensuring safe and convenient access to the elevated living areas. The placement of stairs should consider accessibility for all occupants, including those with mobility impairments. Ramps can provide an alternative means of access for wheelchairs and other assistive devices. The design of railings and handrails should comply with building codes and provide a secure and comfortable grip.
The layout of the interior spaces should take advantage of the natural light and ventilation provided by the elevated position. Large windows and sliding glass doors can maximize views and allow natural light to penetrate deep into the interior. Operable windows and vents can promote cross-ventilation, reducing the need for air conditioning and improving indoor air quality. The placement of rooms should consider the prevailing winds and sun angles, optimizing thermal comfort and reducing energy consumption.
The exterior design of the house should blend harmoniously with the surrounding environment. The selection of materials and colors should complement the natural landscape, creating a cohesive and visually appealing composition. The use of sustainable materials and energy-efficient design strategies can further enhance the environmental friendliness of the house. Green roofs, rainwater harvesting systems, and solar panels can reduce the environmental impact and promote energy independence.
Integrating the house with the surrounding landscape is crucial for creating a seamless transition between the indoor and outdoor spaces. Decks, balconies, and patios can extend the living area outdoors, providing opportunities for relaxation, entertainment, and enjoying the natural environment. Landscaping with native plants can enhance the beauty of the site and provide habitat for local wildlife. Careful consideration of the site contours and drainage patterns can minimize erosion and protect the surrounding ecosystem.
In conclusion, houses on stilts offer a practical and aesthetically pleasing solution for building in areas prone to flooding, unstable soil conditions, or specific geographical constraints. These structures require careful planning and integration of structural, environmental, and architectural considerations. Through detailed site assessments, robust foundation designs, appropriate material selections, and thoughtful architectural planning, houses on stilts can provide safe, comfortable, and sustainable living spaces that harmonize with the natural environment.

Stilt Piling House Plan 2 Bedrooms 1 Baths 1005 Sq Ft Topsider Homes Pge 0101

Piling Pier Stilt Houses Hurricane Coastal Home Plans

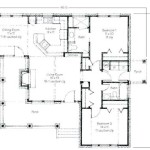
2 Family House Plan On Stilts 62573dj Architectural Designs Plans

120 Best House On Stilts Ideas Beach Plans

Commercial Design Concept Multi Family Stilt Piling Elevated Duplex W 2 Bedrooms Baths Living Room Dining Kitchen And Foyer Collection

Coastal Stilt House Plan With Elevator And Second Level Living Space 765044twn Architectural Designs Plans

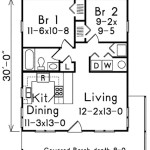
Home Plan Ch464

120 Best House On Stilts Ideas Beach Plans

Elevated Piling And Stilt House Plans Coastal From Home

Cabin Plans On Stilts Pin Up Houses