Duplex House Plans For Small Lots: Optimizing Space and Investment
The escalating cost of land, particularly in urban centers, has spurred a growing interest in innovative housing solutions that maximize space utilization. Duplex house plans, designed specifically for small lots, offer a compelling option for homeowners and investors alike. These plans involve two separate living units within a single structure, allowing for increased density and the potential for rental income or multi-generational living. This article explores the considerations, benefits, and design principles associated with duplex house plans tailored for constrained land areas.
Careful planning and design execution are paramount when constructing a duplex on a small lot. Navigating zoning regulations, minimizing the building footprint, and ensuring privacy for both units are crucial aspects. The success of such a project hinges on a comprehensive understanding of spatial optimization, architectural design principles, and local building codes.
Understanding Zoning Regulations and Lot Restrictions
Before embarking on any duplex construction project, a thorough investigation of local zoning regulations is essential. These regulations dictate numerous factors, including minimum lot size, setback requirements (the distance a building must be from property lines), building height restrictions, and allowable dwelling unit density. Specific zoning classifications might completely prohibit duplexes on certain lots, while others might permit them with specific conditions or requirements. Ignorance of these regulations can result in costly delays, modifications, or even the complete rejection of the building permit application.
Lot coverage, another key factor, dictates the maximum percentage of the lot that can be covered by buildings and impervious surfaces. This limitation directly impacts the size and footprint of the duplex. Additionally, easement restrictions may affect building placement, particularly easements for utilities or shared access. It is advisable to consult with local planning authorities or a qualified land surveyor to obtain accurate information regarding zoning regulations and lot restrictions applicable to the specific property.
Furthermore, parking requirements often vary depending on the number of dwelling units. Duplex construction will typically necessitate providing off-street parking spaces for each unit, which further impacts the available space and design considerations. The availability of street parking and local ordinances regarding parking enforcement should also be factored into the planning process.
Maximizing Space Through Innovative Design
Effective duplex design for small lots necessitates a strategic approach to space optimization. Every square foot should be carefully considered and utilized efficiently. Vertical space should be considered, with multi-story designs often being the most practical solution. Open floor plans, which eliminate unnecessary walls and partitions, can create a sense of spaciousness and improve natural light distribution. Incorporating strategically placed windows and skylights can significantly enhance the perceived size of the living areas.
Shared walls between the two units can save valuable space and reduce construction costs. However, proper soundproofing is crucial to maintain privacy and minimize noise transmission. The use of high-density insulation, resilient channels, and sound-dampening materials in the wall assemblies is highly recommended. Furthermore, staggered stud framing can help to further reduce sound transmission between units.
The layout of the duplex should prioritize functionality and flow. Efficiently designed kitchens and bathrooms are essential, as these areas often consume a significant amount of space. Built-in storage solutions, such as shelving and cabinets, can maximize storage capacity while minimizing clutter. Careful consideration should be given to the placement of staircases, as they can occupy a substantial footprint. Spiral staircases or compact winding stairs can be viable options for smaller spaces, provided they comply with building codes and accessibility requirements.
Outdoor space, even if limited, can significantly enhance the appeal and value of a duplex. Small balconies, patios, or courtyards can provide residents with private outdoor areas for relaxation and recreation. Vertical gardens or green walls can also be incorporated to add greenery and visual interest without consuming valuable ground space.
Ensuring Privacy and Separate Living Spaces
Maintaining privacy between the two units is paramount to the success of a duplex design. Shared entrances and common areas should be avoided whenever possible. Each unit should have its own dedicated entrance, ideally located on opposite sides of the building or at different levels. Separate driveways, walkways, and outdoor areas are also desirable to minimize interaction and maintain a sense of independence for each unit.
The interior layout should be designed to minimize noise transfer between units. Careful placement of bedrooms, bathrooms, and living areas can help to mitigate noise disturbances. As mentioned previously, soundproofing measures are crucial, especially in shared walls and floors. High-quality windows and doors with tight seals can also help to reduce noise transmission from outside. Furthermore, the mechanical systems, such as heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), should be designed to operate independently for each unit to prevent cross-contamination of air and odors.
Consideration should be given to the orientation of the building to maximize natural light and privacy. Strategic placement of windows can provide natural light while minimizing views into neighboring properties or the other unit. The use of landscaping, such as trees and shrubs, can further enhance privacy and create a visual barrier between the units.
Clear delineation of property lines and shared spaces is crucial to avoid disputes between residents. A formal agreement outlining shared responsibilities for maintenance and utilities can help to prevent conflicts and ensure that both units are treated fairly.
Cost-Effective Construction and Material Selection
Controlling construction costs is a significant consideration for any building project, especially when building on a small lot. Careful planning, efficient design, and smart material selection can help to minimize expenses without compromising quality or functionality. Value engineering, which involves analyzing the design and construction processes to identify cost-saving opportunities, is a valuable tool.
Choosing durable and low-maintenance materials can reduce long-term operating costs. Siding materials such as vinyl or fiber cement are relatively inexpensive and require minimal upkeep. Energy-efficient windows and doors can lower utility bills and improve the overall comfort of the units. Sustainable building materials, such as recycled content products and locally sourced materials, can contribute to a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective construction project.
Prefabricated building components, such as walls and roof trusses, can significantly reduce construction time and labor costs. These components are manufactured off-site in a controlled environment, ensuring greater precision and quality control. Modular construction, which involves assembling pre-built modules on-site, can further accelerate the construction process and minimize disruption to the surrounding area.
Efficient use of space and simplified design details can also contribute to cost savings. Avoiding complex rooflines and intricate architectural features can reduce material waste and labor costs. Opting for standard-sized windows and doors can save money compared to custom sizes. A well-defined and detailed construction plan, along with clear communication between the architect, contractor, and homeowner, is essential for minimizing errors and delays, which can significantly impact the overall cost of the project.
Sustainable Design Considerations
Incorporating sustainable design principles into a duplex project on a small lot not only benefits the environment but can also lead to long-term cost savings and increased property value. Energy efficiency, water conservation, and the use of environmentally friendly materials are key considerations.
Energy-efficient design starts with proper insulation to minimize heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. High-performance windows and doors with low U-values (a measure of heat transfer) and low solar heat gain coefficients (SHGC) can significantly reduce energy consumption. Proper orientation of the building to maximize solar exposure in the winter and minimize it in the summer can also contribute to energy savings. The installation of energy-efficient appliances, such as refrigerators, dishwashers, and washing machines, can further reduce energy consumption.
Water conservation measures can include installing low-flow toilets, showerheads, and faucets to reduce water usage. Rainwater harvesting systems can collect rainwater for irrigation or flushing toilets. Drought-tolerant landscaping can minimize the need for irrigation and reduce water bills. Graywater systems, which recycle water from showers and sinks for non-potable uses such as irrigation, can further reduce water consumption.
The use of sustainable building materials, such as reclaimed wood, recycled content products, and sustainably harvested lumber, can minimize the environmental impact of the construction process. Locally sourced materials can reduce transportation costs and support local economies. Non-toxic paints, adhesives, and sealants can improve indoor air quality and reduce exposure to harmful chemicals. Proper waste management during construction is essential to minimize landfill waste and recycle materials whenever possible.
By incorporating these sustainable design considerations, a duplex project on a small lot can be both environmentally responsible and economically viable, offering long-term benefits to both the residents and the community.

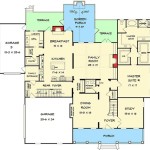
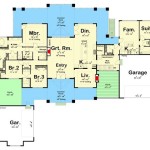
Duplex House Plan For The Small Narrow Lot 67718mg Architectural Designs Plans

Narrow Duplex J1690 15d Plansourceinc Com House Plans Floor

Duplex House Plan For The Narrow Lot 42586db Architectural Designs Plans

Narrow Lot Duplex House Plans 16 Ft Wide Row D 430

Duplex House Plan For The Narrow Lot 42586db Architectural Designs Plans

Narrow Lot Duplex Plan Multi Unit Traditional 3 Beds Per

Plan 2080 Bi Level Duplex Small Or Narrow Lot

J09053d Duplex Plan Plans Floor Container House

Duplex House Plan Ch159d In Modern Architecture

Duplex Townhouse Narrow Lot Skillion Roof House Plans 208