How To Make a House Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
Creating a house plan is a fundamental step in the process of building a new home or renovating an existing one. A well-designed house plan serves as a blueprint for construction, providing detailed information about the layout, dimensions, materials, and systems required for the project. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the process of making a house plan, covering essential steps and considerations for a successful outcome.
The initial phase of creating a house plan involves defining the project's scope and objectives. This includes determining the desired size and style of the house, the number of rooms and their intended functions, and any specific features or amenities required. Thoroughly assessing the needs and preferences of the occupants is crucial to developing a functional and aesthetically pleasing design. Factors such as lifestyle, family size, budget, and site conditions should all be taken into account during this planning stage.
One of the first practical steps is to research relevant building codes and zoning regulations. Local authorities often have specific requirements regarding setbacks, height restrictions, allowable building area, and other aspects of construction. Understanding these regulations is critical to ensure that the house plan complies with all applicable laws and ordinances. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in delays, fines, or even the rejection of the building permit application.
Site analysis is another crucial factor. The characteristics of the building site, such as its topography, soil conditions, orientation, and existing vegetation, can significantly influence the design of the house. A site plan should be created to accurately represent these features and provide a basis for planning the house's placement and orientation on the property. Considerations such as sun exposure, prevailing winds, and drainage patterns should be taken into account to optimize the house's energy efficiency and overall comfort.
Understanding the Needs and Preferences of Occupants
A well-designed house plan must carefully consider the needs and preferences of the people who will be living in the home. This involves understanding their lifestyle, daily routines, and long-term goals. Factors such as the number of occupants, their ages, and any special needs or disabilities should be taken into account. The design should also reflect their personal tastes and preferences in terms of architectural style, interior design, and landscaping.
Analyzing the functional requirements of each room is essential. The kitchen, for example, should be designed with adequate counter space, storage, and appliances to support efficient meal preparation. The living room should be comfortable and inviting, with sufficient seating and appropriate lighting. Bedrooms should be private and restful, with adequate closet space and ventilation. Bathrooms should be functional and accessible, with appropriate fixtures and finishes.
The flow and circulation patterns within the house are also important considerations. The layout should be designed to facilitate easy movement between rooms and minimize unnecessary walking distances. The placement of doors, windows, and hallways should be carefully planned to create a sense of spaciousness and connectivity. The design should also consider the potential for future expansion or modification to accommodate changing needs.
Accessibility is a key design consideration, especially for individuals with disabilities or mobility limitations. The house should be designed to meet the requirements of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) or similar accessibility standards. This includes ensuring that doorways are wide enough to accommodate wheelchairs, that hallways are clear of obstructions, and that bathrooms and kitchens are designed with accessible features.
Developing the Conceptual Design and Floor Plan
Once the preliminary planning and site analysis are complete, the next step is to develop the conceptual design and floor plan. This involves creating a preliminary sketch or drawing of the house layout, showing the placement of rooms, walls, doors, and windows. The conceptual design should reflect the desired size, shape, and style of the house, as well as the specific needs and preferences of the occupants.
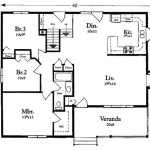
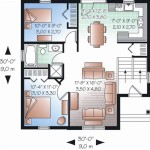
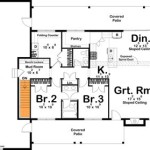
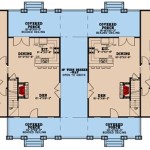
The floor plan is a two-dimensional representation of the house layout, showing the dimensions and relationships of the rooms. It should be drawn to scale and include accurate measurements of all walls, doors, windows, and fixtures. The floor plan should also indicate the location of electrical outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures. The initial floor plan serves as a starting point for further refinement and development.
Several iterations of the floor plan may be required to achieve the desired layout and functionality. It is helpful to use computer-aided design (CAD) software or other drafting tools to create and modify the floor plan. CAD software allows for precise measurements and easy revisions, making it a valuable tool for creating detailed and accurate house plans.
Consider different design options and layouts to explore the possibilities. Experiment with different room arrangements, wall placements, and window sizes to find the optimal configuration. Seek feedback from other stakeholders, such as family members, friends, or design professionals. Incorporate their suggestions and insights to improve the design and ensure that it meets everyone's needs and expectations.
Pay attention to the overall proportions and aesthetics of the house. The design should be visually appealing and harmonious, with a balance of horizontal and vertical elements. Consider the use of architectural features such as porches, balconies, and dormers to add character and interest to the house. The exterior design should complement the surrounding landscape and architecture.
Incorporating Structural and Systems Design
The house plan must incorporate detailed information about the structural and systems design of the house. This includes the foundation, framing, roofing, plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems. Consulting with qualified engineers and contractors is recommended to ensure that these systems are designed and installed correctly and safely.
The foundation design should be based on the site's soil conditions and the house's structural loads. Different types of foundations, such as slab-on-grade, crawl space, or basement, may be appropriate depending on the specific circumstances. The foundation should be designed to provide adequate support and stability for the house, as well as to protect it from moisture and pests.
The framing design should specify the type and size of lumber or steel used for the walls, floors, and roof. The framing should be designed to meet all applicable building codes and structural requirements. The design should also consider the placement of windows and doors, as well as any special structural features such as load-bearing walls or beams.
The roofing design should specify the type of roofing material, the roof slope, and the drainage system. The roofing material should be durable, weather-resistant, and aesthetically pleasing. The roof slope should be designed to effectively shed water and prevent leaks. The drainage system should include gutters and downspouts to direct water away from the foundation.
The plumbing design should specify the location of water lines, drainage pipes, and fixtures. The design should comply with all applicable plumbing codes and regulations. The design should also consider the energy efficiency of the water heating system and the potential for water conservation.
The electrical design should specify the location of electrical outlets, switches, lighting fixtures, and appliances. The design should comply with all applicable electrical codes and regulations. The design should also consider the energy efficiency of the lighting system and the potential for renewable energy sources, such as solar panels.
The HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) design should specify the type of heating and cooling system, the ductwork layout, and the thermostat locations. The design should be energy-efficient and provide comfortable indoor temperatures throughout the year. The design should also consider the ventilation requirements for each room to ensure adequate air quality.
The house plan should include detailed specifications for all materials and finishes used in the construction. This includes the types of flooring, wall coverings, countertops, cabinets, and appliances. The specifications should be clear and unambiguous to avoid any misunderstandings during the construction process.
Creating a comprehensive house plan requires careful planning, attention to detail, and collaboration with qualified professionals. By following these steps and considerations, individuals can create a house plan that meets their needs, complies with all applicable regulations, and results in a functional and aesthetically pleasing home.

Floor Plan Creator And Designer Free Easy App

Floor Plans Types Symbols Examples

Easy To Build Houses And Floor Plans Houseplans Blog Com

Floor Plans Learn How To Design And Plan

How To Create A Floor Plan Before You Move

How To Draw House Plans On Your Pc 5 Simple Steps

Floor Plan Creator And Designer Free Easy App

Make Your Own Blueprint How To Draw Floor Plans

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

How Do You Make A 3d Floor Plan