Understanding Floor Plans for a House
A floor plan is a scaled diagram of a room or building viewed from above. It presents a visual representation of the relationships between rooms, spaces, and other physical features within a structure. Understanding how to read and interpret floor plans is crucial for anyone involved in the design, construction, renovation, or purchase of a house. This detailed guide explores the elements of a floor plan, the different types available, and how to use them effectively.
Key Elements of a Floor Plan
Floor plans are standardized representations, utilizing specific symbols and conventions to convey information efficiently. Mastery of these elements is essential for accurate interpretation.
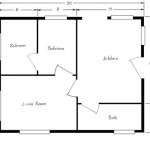
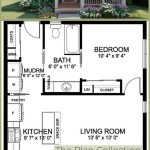
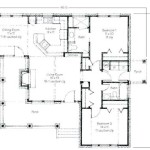
Walls: Walls are typically depicted as thick, solid lines. These lines define the boundaries of rooms and the overall shape of the house. Load-bearing walls, which are crucial for structural integrity, may be indicated differently, often with thicker lines or specific notations. Interior walls, which are non-load-bearing, are usually drawn with thinner lines.
Doors and Windows: Doors are represented by an arc that shows the direction of the door swing. The arc emanates from the hinge point, indicating the space required for the door to open. Different types of doors, such as pocket doors or sliding doors, are depicted with their respective mechanisms. Windows are usually shown as two or three parallel lines within the wall, representing the panes of glass. The size and placement of windows are accurately represented, providing information about natural light and ventilation.
Stairs: Stairs are represented by a series of rectangular steps, with an arrow indicating the direction of ascent. The number of steps and the presence of landings are clearly shown. In some floor plans, the headroom clearance is also indicated, ensuring compliance with building codes.
Fixtures and Appliances: Fixed appliances such as stoves, refrigerators, dishwashers, washing machines, and dryers are drawn to scale and placed in their designated locations. Plumbing fixtures, including sinks, toilets, bathtubs, and showers, are similarly represented. These details provide a clear understanding of the layout and functionality of kitchens and bathrooms.
Dimensions and Measurements: Floor plans include dimensions indicating the length and width of rooms and overall building dimensions. These measurements are generally shown in feet and inches (or meters and centimeters, depending on the region) and are essential for space planning and furniture placement. Overall square footage is also typically provided.
Symbols and Notations: Floor plans use a variety of symbols and notations to represent elements such as electrical outlets, light switches, plumbing pipes, and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems. A legend or key is usually included to explain these symbols, ensuring clarity and accuracy.
Types of Floor Plans
Different types of floor plans serve various purposes, depending on the stage of the project and the information being conveyed. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the appropriate type for a specific need.
Conceptual Floor Plans: These are preliminary sketches that explore different layout possibilities. They are often hand-drawn or created using basic software and are used to brainstorm ideas and refine the overall design concept. Conceptual floor plans focus on the general arrangement of rooms and spaces, without detailed dimensions or specifications.
Detailed Floor Plans: These are precise, scaled drawings that include all the necessary information for construction. They show the exact dimensions of rooms, the placement of doors and windows, the location of fixtures and appliances, and details about the building materials to be used. Detailed floor plans are essential for obtaining building permits and guiding the construction process.
As-Built Floor Plans: These plans document the final configuration of a building after construction is complete. They reflect any changes or modifications made during the construction process and serve as a record of the actual built environment. As-built floor plans are valuable for future renovations or maintenance projects.
Presentation Floor Plans: These are visually appealing plans used for marketing and sales purposes. They are often rendered in color and include furniture layouts, landscaping details, and other features that enhance the visual appeal of the property. Presentation floor plans are designed to showcase the potential of the space and attract prospective buyers or renters.
3D Floor Plans: These plans provide a three-dimensional perspective of the space, allowing viewers to visualize the layout and design in a more realistic way. They are often created using computer-aided design (CAD) software and can be interactive, allowing users to explore the space from different angles and perspectives.
Using Floor Plans Effectively
Effective use of floor plans requires a systematic approach, involving careful analysis and attention to detail. The following guidelines can help in maximizing the value of floor plans during different stages of a project.
Space Planning: Floor plans are essential for space planning, which involves arranging furniture and other elements within a room to maximize functionality and aesthetics. By analyzing the dimensions of rooms and the placement of doors and windows, it is possible to create efficient and comfortable layouts. Consider traffic flow, furniture size, and the intended use of each space when planning the layout.
Visualization: Floor plans help visualize the overall layout and design of a house before construction begins. By studying the plan, it is possible to get a sense of the flow of space, the relationship between rooms, and the overall feel of the house. Use the plan to imagine yourself moving through the space and consider how it will function in daily life. Three-dimensional renderings or virtual tours can further enhance the visualization process.
Communication: Floor plans serve as a communication tool between architects, builders, contractors, and homeowners. By using a common visual language, it is possible to ensure that everyone is on the same page regarding the design and construction of the house. Clearly communicate any questions or concerns about the plan and seek clarification as needed. Document any changes or modifications to the plan to avoid misunderstandings.
Renovation and Remodeling: Floor plans are essential for planning renovations or remodeling projects. By studying the existing floor plan, it is possible to identify potential challenges and opportunities, such as structural limitations or underutilized spaces. Use the plan to experiment with different layouts and configurations before committing to any changes. Ensure that any proposed changes comply with building codes and regulations.
Real Estate Transactions: Floor plans are valuable for real estate transactions, providing potential buyers with a clear understanding of the layout and dimensions of the property. A well-presented floor plan can help buyers visualize the space and make informed decisions. Include a floor plan in any listing materials and be prepared to answer questions about the plan during showings. The floor plan should accurately reflect the current condition of the property.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Floor plans play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with building codes and regulations. Accurate and detailed floor plans are required for obtaining building permits and demonstrating that the proposed construction meets all applicable standards. Verify that the floor plan includes all necessary information, such as fire safety features, accessibility requirements, and structural details. Consult with a qualified architect or engineer to ensure compliance with all relevant codes and regulations.
Floor plans are a fundamental tool in the design and construction industry. Their ability to convey spatial information clearly and concisely makes them indispensable for a wide range of applications, from initial conceptualization to final construction and beyond. A comprehensive understanding of floor plan elements, types, and applications empowers individuals to participate effectively in the creation and modification of residential spaces.
By mastering the art of reading and interpreting floor plans, individuals can make informed decisions, communicate effectively, and contribute to the successful realization of their housing aspirations.

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

Traditional Style House Plan 4 Beds 3 5 Baths 3659 Sq Ft 81 13837 How To Plans Monster

Peach Tree House Plan Ranch Floor Designs

Draft 2d Floor Plans House Elevation And Redraw To Autocad Cad Dwg

Durham Drive Craftsman House Plans Ranch

Living Options Webster House

Floor Plans Types Symbols Examples

House Plan 94300 Quality Plans From Ahmann Design

Easy To Build Houses And Floor Plans Houseplans Blog Com