Floor Plans For Existing Homes: A Comprehensive Guide
Creating or acquiring floor plans for existing homes is a multifaceted undertaking, often required for renovation projects, property valuation, insurance purposes, or simply for personal record-keeping. Understanding the different methods for obtaining these plans, the information they contain, and their potential applications is crucial for homeowners, contractors, and real estate professionals alike. The process can range from easily retrieving archived plans to employing specialized surveying techniques, depending on the age of the home, local regulations, and the homeowner's specific needs.
The absence of readily available floor plans shouldn't deter homeowners from pursuing them. While new construction projects generally require detailed floor plans approved by local building authorities, older homes might lack such documentation, or the original plans might be lost or destroyed. This necessitates exploring alternative methods for recreating or approximating the floor plan as accurately as possible.
Understanding the Importance of Floor Plans
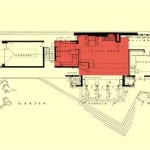
Floor plans serve as a visual representation of a home's layout, dimensions, and features. They provide a bird's-eye view of the structure, illustrating the arrangement of rooms, walls, doors, windows, and sometimes even built-in fixtures. This detailed depiction is invaluable for several reasons. Firstly, it facilitates space planning and design. Homeowners can use floor plans to experiment with furniture arrangements, visualize potential remodeling projects, and assess the feasibility of adding new features or altering existing spaces. This proactive approach can save time and money by preventing costly mistakes during renovation.
Secondly, floor plans are essential for obtaining building permits for renovations. Local building codes typically require detailed plans to ensure that the proposed changes comply with safety regulations, zoning laws, and accessibility standards. Without accurate floor plans, obtaining the necessary permits can be significantly delayed or even denied. The plans allow inspectors to assess the structural integrity of proposed modifications and verify compliance with relevant codes.
Thirdly, floor plans are beneficial for insurance purposes. In the event of damage or loss due to fire, flood, or other disasters, having a detailed floor plan can help insurance adjusters accurately assess the extent of the damage and expedite the claims process. The plan provides a clear record of the home's layout and features, allowing for a more precise and efficient assessment of repair or replacement costs.
Finally, floor plans add value to a property when it is being sold. Potential buyers can use the plans to visualize themselves living in the space, plan furniture arrangements, and assess the home's suitability for their needs. A well-presented floor plan can be a powerful marketing tool, showcasing the home's features and layout in a clear and compelling manner. Furthermore, it demonstrates the homeowner's attention to detail and enhances the perceived value of the property.
Methods for Obtaining or Creating Floor Plans
Several methods can be employed to obtain or create floor plans for existing homes. The most appropriate approach depends on the availability of existing documentation, the desired level of accuracy, and the homeowner's budget. The following methods are commonly used:
1. Checking Local Records: The first step is to check with local government agencies, such as the building department or the county recorder's office. These agencies often maintain archives of building permits and associated documents, including floor plans. Original plans submitted during the home's construction might be on file, providing a ready-made solution. Accessing these records is typically a straightforward process, although fees may apply for copies or searches. In some cases, the information may be available online through the agency's website.
2. Reviewing Mortgage or Appraisal Documents: Mortgage lenders and appraisers often require floor plans as part of their assessment process. Reviewing existing mortgage or appraisal documents might reveal the presence of floor plans. These plans may not be as detailed as architectural drawings, but they can provide a basic outline of the home's layout and dimensions. Contacting the lender or appraiser who handled the original transaction can be a fruitful avenue for obtaining these documents.
3. Hiring a Professional Surveyor or Architect: If existing plans are unavailable, hiring a professional surveyor or architect is the most accurate solution. Surveyors use specialized equipment, such as laser scanners and measuring tapes, to precisely measure the dimensions of the home and create a detailed floor plan. Architects can then take the surveyor's measurements and create professional-grade drawings that are suitable for construction or renovation purposes. This method is more expensive than other options, but it ensures accuracy and compliance with building codes.
4. Using DIY Measurement Tools and Software: Homeowners can create their own floor plans using DIY measurement tools and software applications. Laser distance measurers and measuring tapes can be used to measure the dimensions of each room. These measurements can then be input into floor plan software, which automatically generates a visual representation of the home's layout. Several software options are available, ranging from free online tools to more sophisticated programs that require a subscription. While this method is less accurate than hiring a professional, it can be a cost-effective solution for basic floor planning purposes.
5. Employing 3D Scanning Technology: Advancements in technology have made 3D scanning an increasingly viable option for creating floor plans. Handheld 3D scanners can be used to capture detailed measurements and create a three-dimensional model of the home's interior. This model can then be used to generate accurate floor plans and even virtual tours of the property. While 3D scanning technology is still relatively expensive, it offers a high level of accuracy and detail. Several companies specialize in providing 3D scanning services for residential properties.
Key Considerations When Creating or Utilizing Floor Plans
Several key considerations should be kept in mind when creating or utilizing floor plans for existing homes. These considerations relate to accuracy, scale, completeness, and accessibility.
1. Accuracy and Precision: The accuracy of the floor plan is paramount, especially when using it for renovation or construction purposes. Inaccurate measurements can lead to costly mistakes and delays. Using professional surveying or architectural services ensures the highest level of accuracy. When using DIY methods, careful attention to detail and multiple measurements are essential. It is also important to account for irregularities in the walls, such as angles and curves, to ensure that the floor plan accurately reflects the home's actual dimensions.
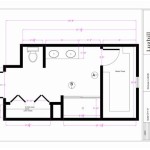
2. Scale and Representation: Floor plans are typically drawn to scale, meaning that the dimensions are proportional to the actual size of the home. Common scales include 1/4 inch to 1 foot or 1/8 inch to 1 foot. Understanding the scale is crucial for interpreting the plan and accurately estimating the size of rooms and features. The floor plan should also clearly indicate the direction of north, which is essential for understanding the building's orientation and natural light exposure.
3. Completeness of Information: A complete floor plan should include all essential information, such as the location of walls, doors, windows, and fixtures. It should also indicate the dimensions of each room, the overall dimensions of the home, and the location of any structural elements, such as columns or beams. Furthermore, the plan should include labels for each room and any other relevant features, such as closets, staircases, and fireplaces. A comprehensive floor plan provides a complete picture of the home's layout and features.
4. Accessibility and Format: The floor plan should be easily accessible and available in a format that can be readily shared with contractors, architects, and other professionals. Digital formats, such as PDF or DWG, are ideal for sharing and editing. It is also important to ensure that the floor plan is clearly labeled and organized, making it easy for others to understand and use. Consider creating multiple versions of the floor plan, with varying levels of detail, to suit different purposes.
5. Legal and Regulatory Compliance: When using floor plans for renovation or construction projects, it is essential to ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations. The plans should be reviewed by a licensed architect or engineer to ensure that they meet all applicable requirements. Obtaining the necessary permits and approvals before starting any work is crucial to avoid potential legal issues and ensure the safety of the project. Failure to comply with building codes can result in fines, delays, and even the demolition of non-compliant structures.
In conclusion, obtaining or creating floor plans for existing homes is a crucial step in various real estate and home improvement endeavors. The method chosen should align with the project's requirements, budget, and desired accuracy level. Whether leveraging existing records, employing professional services, or opting for DIY solutions, a well-executed floor plan provides a valuable asset for homeowners and professionals alike.

Home Addition Plan 6232

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

Great Room Addition Plan Post And Beam Barn Style Homes Plans Home Bedroom

Add A Floor Convert Single Story Houses Home Addition Plans Two House Bedroom

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

Interior Design Floor Plan Before After Reed

House Plans How To Design Your Home Plan

Where You Can Buy House Plans Live Home 3d